貨號(hào)
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價(jià)
備注
BN41253R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
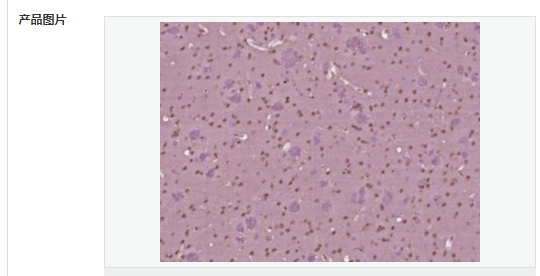
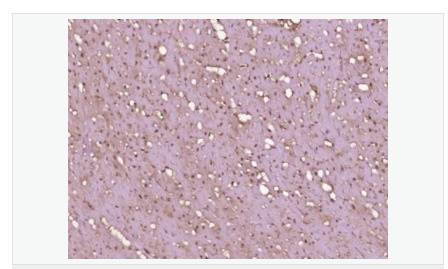
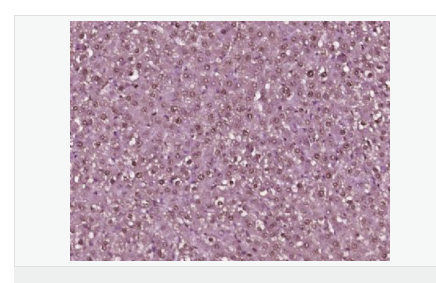
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) 推薦應(yīng)用:IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,ELISA
BN41253R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human,Mouse,Rat(predicted:Dog,Pig,Cow,Horse,Rabbit,Sheep) 推薦應(yīng)用:IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
| 英文名稱 | NOTCH4 |
| 中文名稱 | 跨膜蛋白NOTCH4配體抗體 |
| 別 名 | Notch 4; FLJ16302; hNotch 4; hNotch4; INT 3; INT3; MGC74442; Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 4; NOTC4_HUMAN; NOTCH 3; NOTCH 4; Notch 4 intracellular domain; Notch homolog 4; NOTCH3; Notch4; NOTCH4 protein; OTTHUMP00000062678. |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 心血管 細(xì)胞生物 神經(jīng)生物學(xué) 信號(hào)轉(zhuǎn)導(dǎo) 細(xì)胞膜受體 表觀遺傳學(xué) 跨膜蛋白 |
| 抗體來(lái)源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Mouse, Rat, (predicted: Human, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Rabbit, Sheep, ) |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復(fù)) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 207kDa |
| 細(xì)胞定位 | 細(xì)胞核 細(xì)胞膜 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human NOTCH4:1151-1250/2003 <Extracellular> |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲(chǔ) 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | This gene encodes a member of the Notch family. Members of this Type 1 transmembrane protein family share structural characteristics including an extracellular domain consisting of multiple epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats, and an intracellular domain consisting of multiple, different domain types. Notch family members play a role in a variety of developmental processes by controlling cell fate decisions. The Notch signaling network is an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling pathway which regulates interactions between physically adjacent cells. In Drosophilia, notch interaction with its cell-bound ligands (delta, serrate) establishes an intercellular signaling pathway that plays a key role in development. Homologues of the notch-ligands have also been identified in human, but precise interactions between these ligands and the human notch homologues remain to be determined. This protein is cleaved in the trans-Golgi network, and presented on the cell surface as a heterodimer. This protein functions as a receptor for membrane bound ligands, and may play a role in vascular, renal and hepatic development. This gene may be associated with susceptibility to schizophrenia in a small portion of cases. An alternative splice variant has been described but its biological nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] Function: Functions as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands Jagged1, Jagged2 and Delta1 to regulate cell-fate determination. Upon ligand activation through the released notch intracellular domain (NICD) it forms a transcriptional activator complex with RBPJ/RBPSUH and activates genes of the enhancer of split locus. Affects the implementation of differentiation, proliferation and apoptotic programs. May regulate branching morphogenesis in the developing vascular system. Subcellular Location: Cell membrane and Nucleus. Following proteolytical processing NICD is translocated to the nucleus. Tissue Specificity: Highly expressed in the heart, moderately in the lung and placenta and at low levels in the liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, pancreas, spleen, lymph node, thymus, bone marrow and fetal liver. No expression was seen in adult brain or peripheral blood leukocytes. Post-translational modifications: Synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum as an inactive form which is proteolytically cleaved by a furin-like convertase in the trans-Golgi network before it reaches the plasma membrane to yield an active, ligand-accessible form. Cleavage results in a C-terminal fragment N(TM) and a N-terminal fragment N(EC). Following ligand binding, it is cleaved by TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) to yield a membrane-associated intermediate fragment called notch extracellular truncation (NEXT). This fragment is then cleaved by presenilin dependent gamma-secretase to release a notch-derived peptide containing the intracellular domain (NICD) from the membrane. Phosphorylated. Similarity: Belongs to the NOTCH family. Contains 5 ANK repeats. Contains 28 EGF-like domains. Contains 3 LNR (Lin/Notch) repeats. SWISS: Q99466 Gene ID: 4855 Database links: Entrez Gene: 4855 Human Omim: 164951 Human SwissProt: Q99466 Human Unigene: 436100 Human Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |